Trees
A tree is a nonlinear hierarchical data structure that consists of nodes connected by edges.
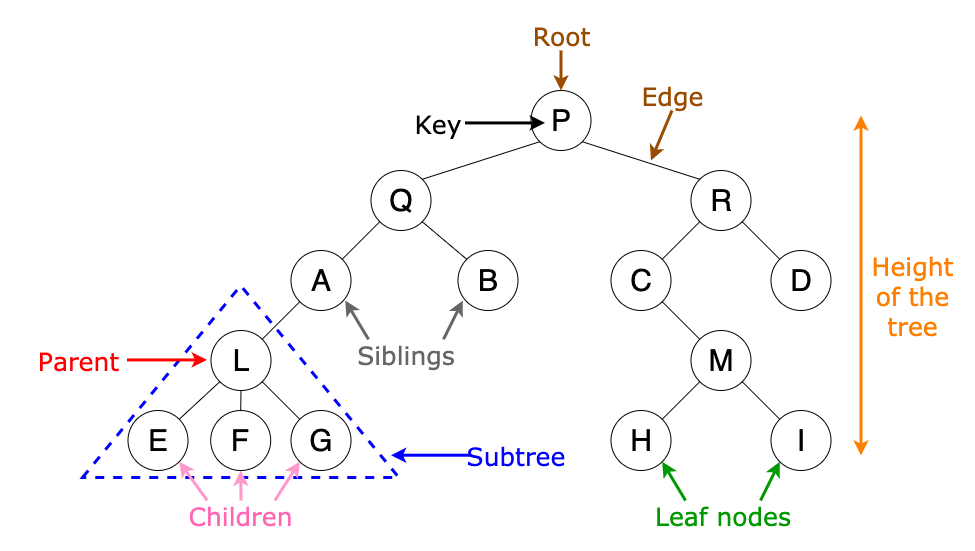
Common Terminology
Node:
A Tree node is a component which may contain it’s own values, and references to other nodes.
Root:
The root is the node at the beginning of the tree.
K:
A number that specifies the maximum number of children any node may have in a k-ary tree. In a binary tree, k = 2.
Left:
A reference to one child node, in a binary tree.
Right:
A reference to the other child node, in a binary tree.
Edge:
The edge in a tree is the link between a parent and child node.
Leaf:
A leaf is a node that does not have any children.
Height:
The height of a tree is the number of edges from the root to the furthest leaf.
Binary Tree Data Structure
Binary Tree Data Structure has elements and each elemnt has at most 2 children and each child called left and right child. Each Node contains:
- Data
- Pointer to left child
- Pointer to right child
Traversals:
- Traversing a tree allows us to search for a node and print out the contents of a tree.
- Tree Traversing ways:
- Depth First
- Breadth First
Depth First
Depth first traversal is where we prioritize going through the height of the tree first. There are three methods for depth first traversal:
- Pre-order:
root >> left >> right - In-order:
left >> root >> right - Post-order:
left >> right >> root